Deputy Mayor’s Office for Economy, SMG
Nobody can see the future
It may not be possible to paint a complete picture of the impacts of COVID-19 around the world. Nobody has been able to determine the start and end points of the virus. Moreover, since the modern world has become intensively globalized, it has been difficult for economies and humans to avoid the COVID-19 pandemic.
No person or country is likely to remain untouched by the impacts of this pandemic. Therefore, every economy, city, and country must be on high alert to suppress the spread of COVID-19 and reinforce the whole societal system.
Overall response system in Korea
In Korea, the government has three tiers: the central government, regional governments like the Seoul Metropolitan Government (SMG) and Gyeonggi-do Province, and local bodies such as Gangnam District.
At the central government level, the Central Accident Investigation Headquarters (CAIH), managed by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, and the Central Discharge Countermeasures Headquarters (CDCH), managed by the Korean Center for Disease Control (KCDC), play a significant role in overall policy-making and comprehensively managing the whole process to suppress the epidemics like COVID-19.
In the KCDC, there are five special disease control centers, five research centers, and four planning and administration divisions, and their main roles are as follows.
- Operate an exhaustive response system for new infectious diseases
- Strengthen the operation of the national infectious disease surveillance system
- Eradicate tuberculosis, which is more common in low-income countries, earlier
- Build a platform for analyzing bio-medical science information
- Establish an organizational system to respond to the ever-changing environment
Seoul Metropolitan City has nine public general hospitals. It also has 53 public health centers, including branches within the city, which play an important role in maintaining public health.
Current status of COVID-19 in Korea
Epidemiological analysis has been performed via three screening points:
- COVID-19 special screening centers: Nationwide 611; Seoul 72
- Drive-through screening centers: Nationwide 79; Seoul 4
- Public healthcare centers including branches: Nationwide 3,550; Seoul 53
Individuals who do not have a respiratory disease but have other diseases, such as cancer or cardiovascular disease, can easily visit any of the 334 specially-designated public relief hospitals nationwide. If respiratory symptoms appear and when COVID-19 is suspected, individuals can get a consultation by calling the COVID-19 Emergency 1339 call center or visiting their public health center first, and then visiting the COVID-19 special screening centers.
Seoul and Korea have implemented comprehensive countermeasures
The SMG and the Korean Central Government have implemented measures to contain and curb this unprecedented virus. On January 20th 2020, the first COVID 19 case was confirmed and the Korean Central Government broadcasted its first caution-level message to the public. Next, an alert-level message was delivered on January 28th 2020. Finally, on February 23rd 2020, Korean society was confronted with the serious stage of the epidemic.
Even before broadcasting the first caution-level message, the central government had set up an immediate response taskforce (T/F) within the KCDC on January 3rd 2020 to monitor the spread of COVID-19. Subsequently, it scaled up its monitoring system from the T/F to the CDCH and the Central Disaster and Safety Countermeasures (CDSC) Headquarters, presided by Prime Minister, in response to the progress of COVID-19.
Meanwhile, the SMG and private sectors, such as companies and hospitals, have made efforts to implement these comprehensive countermeasures by providing their public health infrastructure for initial consultations and more in-depth screening, and business products for epidemiological investigations.
Additionally, South Korea was the first country to introduce new innovative ideas, such as the “Drive-Thru Screening Center” in Daegu Metropolitan City and the “Phone Booth Virus Testing Center,” making testing seven times quicker than previous regular tests conducted in Seoul, into the testing process .
With the help of the public-private partnerships and innovative ideas, Seoul and Korea have effectively handled the COVID-19 outbreak and the total number of confirmed cases has remained stable since March 16th 2020.
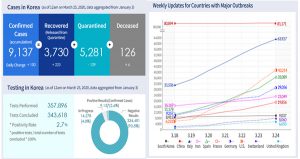
Confirmed cases: 9,137 (accumulated) = recovered: 3,730 + quarantined: 5,281 + deceased: 126
▶ Quick Test – Rapid Response
Real-time genetic tests (RT-PCR tests), developed by Korean companies, have been used to diagnose COVID-19, through the extraction of the virus’s genetic code.
Several social and medical resources have been comprehensively mobilized to contain the spread of COVID-19, including drive-through screening centers, COVID-19 screening centers, and public relief hospitals.
A self-diagnosis mobile app is being utilized to monitor international travelers from their entry points in Korean airports throughout their daily lives in Korea. All travelers are required to install the self diagnosis mobile app and record their daily health status on the app for 14 days after their arrival in Korea.
▶ Transparency – Comprehensive Societal Participation
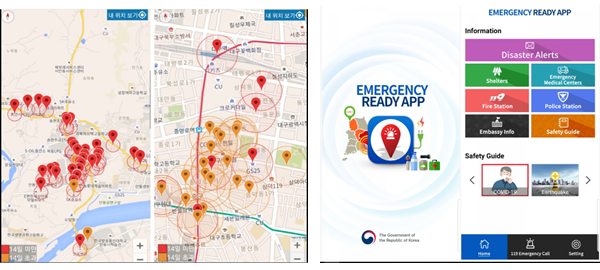
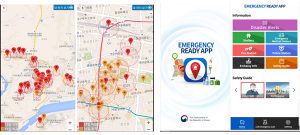
All data related to COVID-19, including confirmed cases and monitoring data of close contacts, are fully accessible by the public and the world. Regional governments and local bodies are sending this data via mobiles to the public round the clock to help citizens stay away from local infection.
The Corona 100m app was developed by a Seoul-based startup, a company that specialized in 3D graphics. This app informs citizens of known COVID-19 cases and stores selling facial masks within 100 meters of their location.
Emergency Ready, distributed by the Ministry of Interior and Safety, is an app targeted toward foreign residents and which provides useful information regarding emergency shelters, medical centers, fire stations, emergency medical centers, police stations, and safety guides.
The SMG announced its support for the “social distancing campaign,” suggested by the Korean Medical Association, on February 28th 2020. As a first step, the SMG shut down open spaces within startup incubating facilities and introduced a “work from home” (WFH) strategy within the SMG’s organizations. Moreover, it encouraged the private sector to participate in its WFH and remote work campaign.
The second step involved comprehensive screening of overcrowded business sites, such as customer service centers, micro-companies with under five employees, and entertainment facilities, such as Internet cafés and singing rooms, within its area from March 11th 2020 onwards. The SMG screened more than 11,000 sites. Simultaneously, 27,000 people were mobilized for the preemptive prevention task against epidemics in 350 conventional markets.
The impact of COVID-19 on Startup Ecosystem already started
In Korea, the number of investment deals in February 2020 dropped to a fifth, i.e., 10 deals worth $255 million, of that in the previous month. China also experienced a difficult time in January and February 2020, when it faced a 62% drop in investment, compared to the same period in the previous year. The main reason for this was the drastic reduction in “face-to-face meetings” between startups and their investors.
The global business ecosystem became aware of the weaknesses of the global manufacturing value chain. Therefore, ecosystem experts anticipate that countries with low-cost labor would serve as other potential value chains in the global economy.
Some industrial sectors, such as Robots, drones, bio-medical devices, healthcare, AI-applied systems, online platforms, are benefiting from this unexpected situation, while others are experiencing a hard “winter season.” In particular, AI-based systems, healthcare, and online shops are in a relatively good position. Moreover, careful opinions are arising from Korea’s domestic market that anticipate the impact of COVID-19 on the startup ecosystem will be less than expected, owing to its strong foundation and fueled by public funds.
How to overcome the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the Startup Ecosystem
1. Non-fiscal measures
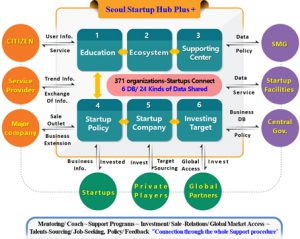
▶ Online virtual ecosystem: Seoul Startup Hub Plus +
All players, such as startups, accelerators, venture capitalists, and service providers, in the startup ecosystem will participate in this virtual system and create new value that will be shared among them with less “face-to-face” contact.
√ (Startups will receive) funding and access to global markets, and scale up their operations
√ (Global companies can source) technologies and talent to maximize their profits
√ (Investors will be able to identify) promising and excellent startups
Data entry work has been implemented from August 2019 to March 2020. The system to be developed will be demonstrated in April 2020 and launched in May 2020.
▶ Online Startup Big Match: Preliminary Promotion Event for Tech-Rise 2020
This is a video-conference-type exposure event for startups, wherein global players as well as big domestic players will participate, and which will be held in Seoul. This event will expose excellent Korean startups to the world via the Internet. The preparation and match making process will be undertaken from April to May 2020 and the event will be broadcast in late June, 2020.
▶ Support for Startups in Preparation for the Post-COVID-19 Period
The Seoul Business Agency, a foundation funded by the SMG, has been developing a new brand for products and services provided by Seoul-based startups for the past two years: “Seoul-made,” which represents high quality and reasonable prices for potential customers in the global market.
Localization of the brand has been implemented since 2019 in Vietnam, Thailand, Singapore, South America, and North America. A total of 500 “Seoul-made” startups have collaborated with six major local distributors to extend the scale of their sales in these markets.
Additionally, the SMG has implemented a public testbed program to support startups related to fourth-industrial-revolution technologies to overcome the global economic impact of COVID-19. Moreover, the Seoul Global Challenge Project, which is a global startup competition for discovering promising new urban tech startups, will be initiated in the second half of 2020.
2. Financial and fiscal measures
▶ Central Government: $850 billion Economy Stimulus Package announced
The central government has implemented an economic policy to provide sufficient liquidity for markets and to deploy stability tools to absorb financial shocks amid the COVID-19 pandemic.
It has implemented two strategies in collaboration with financial institutions: First, financial support of $47 billion will be provided to enterprises, which will enable them to deal with cash flow difficulties and borrow money at the lowest interest rate of 1.5% from any financial institution. Second, a financial stability package of $38 billion will be provided to financial markets, which includes the bond market and stock market stabilization funds.
The $47 billion financial support, there have been the business emergency funds, special loan guarantee program, credit recovery support, primary collateralized bond obligations (P-CBOs) for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). From March 24th 2020, the range of the enterprises will be extended to large firms and middle-sized businesses.
To this end, the central government determined the first extra and supplementary budget in 2020 of about $9.5 billion and it will be used for dealing with the COVID-19 outbreak and minimizing any economic fallout in early March, From the budget, nearly $1.1 billion will be spent to provide financial support for SMEs to deal with financial difficulties. Additionally, $486 million will be provided to maintain employment in SMEs and $80 million will be used for the effective implementation of the loan guarantee program.
On March 19th 2020, the central government decided to raise two separate funds to stabilize the country’s bond and stock markets. The bond stabilization fund was increased from $7.7 billion to $15.4 billion and the stock stabilization fund was $8.8 billion.
In addition to these funds, the government will issue primary collateralized bond obligations (P-CBOs) worth $5.3 billion over the next three years to support businesses with relatively lower credit ratings.
Regarding the extension of tax payment and return periods, the National Tax Service will provide support to individual companies based on their financial situations.
▶ Seoul Metropolitan Government’s Measures
The SMG has implemented measures to minimize the impact of COVID-19 on the local economy and to effectively support SMEs to overcome the economic impact caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
As a first move, 872 million-worth Emergency Fund for SMEs has been distributed into 18 kinds of small businesses such as travel agencies, restaurants, and motels, which are regarded as the severest-impacted sectors. Additionally, to boost demand in local economy, the SMG has issued a “Seoul- Neighborhood-Mobile Voucher” at a 20% discounted rate.
From the annual budget, excluding personnel expenditure and the reserve budget, 62.5% or $17.2 billion will be spent immediately in the first half of the year to fulfill contracts earlier or for a much speedier procurement process. This tax money will be transferred to the private sector to be used for the revitalization of the local economy.
For startups with less than five employees and that are facing difficulties, the Employment Maintain Subsidy will be provided at a maximum of $400 per person per month for two months. This will help startups keep their staff employed. This subsidy amounts to $16 million and nearly 20,000 employees will benefit from it.
Specially-Targeted Business Accelerating Fund, i.e., a maximum of $240,000 per startup, will be invested in startups. This equity fund will be funded by the Seoul Business Agency from June 2020 onwards. A total of $12 million will be invested in 50 promising startups.
Startups, that are being incubated within Seoul’s 25 public facilities, will benefit from a partial rent exemption and an extension of stay, provided that these startups agree to the participate in the social distancing campaign.
Regarding tax administration, Seoul will provide an extended period for tax payments and tax returns for startups and SMEs which have been in difficulties of cash flow.
In addition to these urgent measures, the SMG has planned a second round of comprehensive measures, including direct subsidies for SMEs that have been impacted by COVID-19, and will be announcing it soon.
Source: http://english.seoul.go.kr/covid-19-and-countermeasures-in-seoul/





![SEOUL [Intensive “Social Distancing,” a Battle between Life and Death]](https://capitalsinitiative.com/wp-content/uploads/thumbs_dir/여의도한강공원아이서울유-scaled-1whq2o5fygxtjuebtqvyxu83ki3lofgdt1tpan9vhin8.jpg)
